The GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) provides organizations that process data through cloud services with some unique challenges and opportunities.
The GDPR aims primarily to give control back to citizens and residents over their personal data, and it will begin to take effect on 25 May 2018.
Before talking about the GDPR obligations, let us talk a little bit about the cloud shared responsibility model:
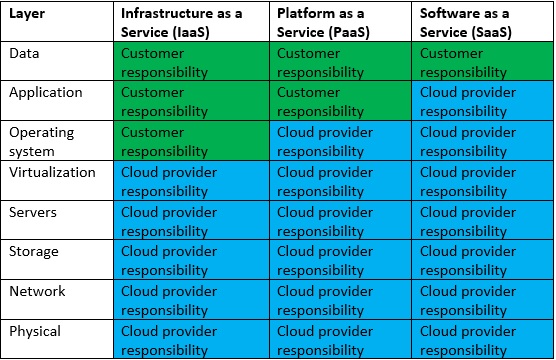
From the above table it is easier to understand that both the customer and the cloud service provider have clear responsibilities.
The cloud service provider is responsible for the physical protection (and data center locations) and over the infrastructure layers (beside the operating system in IaaS model).
The customer is the data owner, and as such, he is responsible for access permissions and auditing. On IaaS and PaaS models, the customer is also responsible for the application layer in terms of access controls, hardening and configuration, encryption, etc.
This model is important to understand, because the GDPR has specific requirements that the cloud service provider is not responsible for, and any organization storing/processing private data, needs to be aware of and prepare accordingly in-order to be compliant with the GDPR.
Main GDPR requirements related to cloud services:
- Know the location where cloud applications are processing or storing data.
- Perform an inventory of all your organization cloud services and compare them with the cloud service provider’s official web sites, regarding compliance with the GDPR. For example:
- Microsoft – https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/TrustCenter/Privacy/gdpr/default.aspx
- AWS – https://aws.amazon.com/compliance/gdpr-center/
- Google – https://www.google.com/cloud/security/gdpr/
- IBM – https://www.ibm.com/security/data-security/gdpr
- Oracle – https://www.oracle.com/applications/gdpr/index.html
- Salesforce – https://www.salesforce.com/eu/campaign/gdpr/
- Use discovery tools, to locate where sensitive (GDPR related personal data) is located on your cloud services. For example:
- Microsoft Azure Data Catalog – https://azure.microsoft.com/en-gb/services/data-catalog/
- Perform an inventory of all your organization cloud services and compare them with the cloud service provider’s official web sites, regarding compliance with the GDPR. For example:
- Protect personal data:
- Use strong authentication (Multi-factor authentication). For example:
- Monitor security incidents. For example:
- Encrypt data at rest. For example:
- Microsoft: https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/key-vault/
- AWS – https://aws.amazon.com/kms/
- Google – https://cloud.google.com/kms/
- Oracle – https://docs.oracle.com/en/cloud/get-started/subscriptions-cloud/mmocs/controllingtde-keys.html
- Salesforce – https://developer.salesforce.com/docs/atlas.en-us.securityImplGuide.meta/securityImplGuide/security_pe_byok.htm
- Control who has access to your data in the cloud. For example:
- Data processing agreement (DPA):
- Sign a data processing agreement with the cloud service providers, to make sure they properly protect personal data and they commit not to move data outside the EU. For example:
- Microsoft – http://www.microsoftvolumelicensing.com/Downloader.aspx?DocumentId=13022
- AWS – https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/security/tag/data-processing-agreement/
- Google – https://cloud.google.com/terms/data-processing-terms
- Salesforce – https://www.salesforce.com/assets/pdf/misc/data-processing-addendum.pdf
- Check the compliance of the cloud service provider against known security standards. For example:
- Microsoft – https://cloudsecurityalliance.org/star-registrant/microsoft/
- AWS – https://cloudsecurityalliance.org/star-registrant/amazon-aws/
- Google – https://cloudsecurityalliance.org/star-registrant/google/
- Salesforce – https://cloudsecurityalliance.org/star-registrant/salesforce-com-inc/
- IBM – https://cloudsecurityalliance.org/star-registrant/ibm-cloud/
- Sign a data processing agreement with the cloud service providers, to make sure they properly protect personal data and they commit not to move data outside the EU. For example:
Eyal Estrin
Eyal Estrin is a Cloud Architect.
He joined IUCC in December 2017 and his main focus is promoting and supporting cloud services in Universities in Israel. He brings with him more than 20 years of experience in the IT and information security field.
Follow him at @eyalestrin